
Is present in natural sources of helium with a smaller abundance than that of any other stable isotope relative Of 0.000 137 % as determined by Nier had a negligible effect on the atomic weight of helium. The atomic mass of 4He to four decimal places. In its 1961 report, the Commission recommended A r(He) = 4.0026 based on Helium – Properties Summary Element Helium Atomic Number 2 Symbol He Element Category Noble Gas Phase at STP Gas Atomic Mass 4.0026 Density at STP 0.1785 Electron Configuration 1s2 Possible Oxidation States 0 Electron Affinity - Electronegativity - 1st Ionization Energy 24.5874 Year of Discovery 1895 Discoverer Ramsey, Sir William & Cleve, Per Teodor Thermal properties Melting Point -272.2 Boiling Point -268.9 Thermal Conductivity 0.1513 Specific Heat 5.193 Heat of Fusion - Heat of Vaporization 0.In contrast to the other noble gases, which are separated for commercial use almost entirely fromĪir, a large amount of commercial He is derived from natural gas deposits containing relatively high concentrations The Standard English unit is pounds mass per cubic foot ( lbm/ft 3). The standard SI unit is kilograms per cubic meter ( kg/m 3). In other words, the density (ρ) of a substance is the total mass (m) of that substance divided by the total volume (V) occupied by that substance. It is an intensive property, which is mathematically defined as mass divided by volume: Typical densities of various substances at atmospheric pressure.ĭensity is defined as the mass per unit volume. How does the atomic mass determine the density of materials? Density of Helium The atomic mass number determines especially the atomic mass of atoms. The mass number is different for each different isotope of a chemical element.
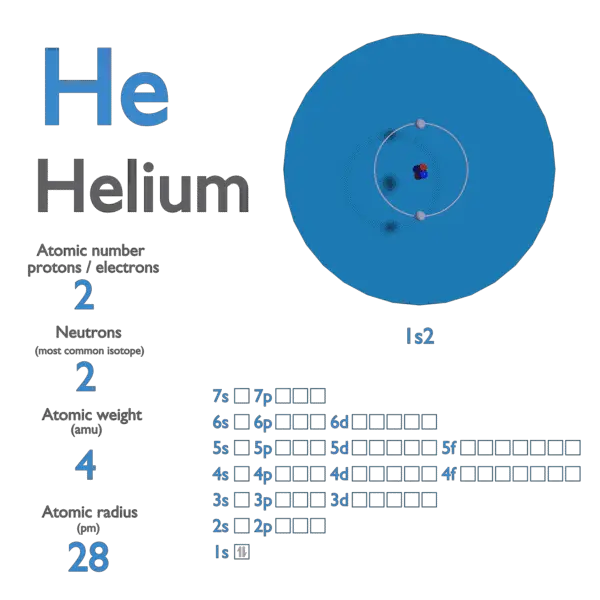
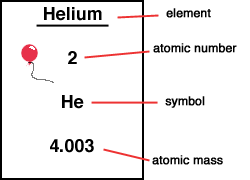
For 63Cu, the atomic mass is less than 63, so this must be the dominant factor. A nucleus with greater binding energy has lower total energy, and therefore a lower mass according to Einstein’s mass-energy equivalence relation E = mc 2. The nuclear binding energy varies between nuclei.This increases the mass of nuclei with more neutrons than protons relative to the atomic mass unit scale based on 12C with equal numbers of protons and neutrons. The neutron is slightly heavier than the proton.There are two reasons for the difference between mass number and isotopic mass, known as the mass defect: For example, 63Cu (29 protons and 34 neutrons) has a mass number of 63, and an isotopic mass in its nuclear ground state is 62.91367 u. For other isotopes, the isotopic mass usually differs and is usually within 0.1 u of the mass number. One unified atomic mass unit is approximately the mass of one nucleon (either a single proton or neutron) and is numerically equivalent to 1 g/mol.įor 12C, the atomic mass is exactly 12u, since the atomic mass unit is defined from it. One atomic mass unit is equal to 1.66 x 10 -24 grams. The unit of measure for mass is the atomic mass unit (amu). Therefore this resulting atomic mass is calculated from naturally-occurring isotopes and their abundance. Note that each element may contain more isotopes. How does the atomic number determine the chemical behavior of atoms? Atomic Mass of Helium Since the number of electrons is responsible for the chemical behavior of atoms, the atomic number identifies the various chemical elements. Helium is a chemical element with atomic number 2 which means there are 2 protons and 2 electrons in the atomic structure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
